Manitou Forest Observatory
MFO Site Information
|
Page contents: |
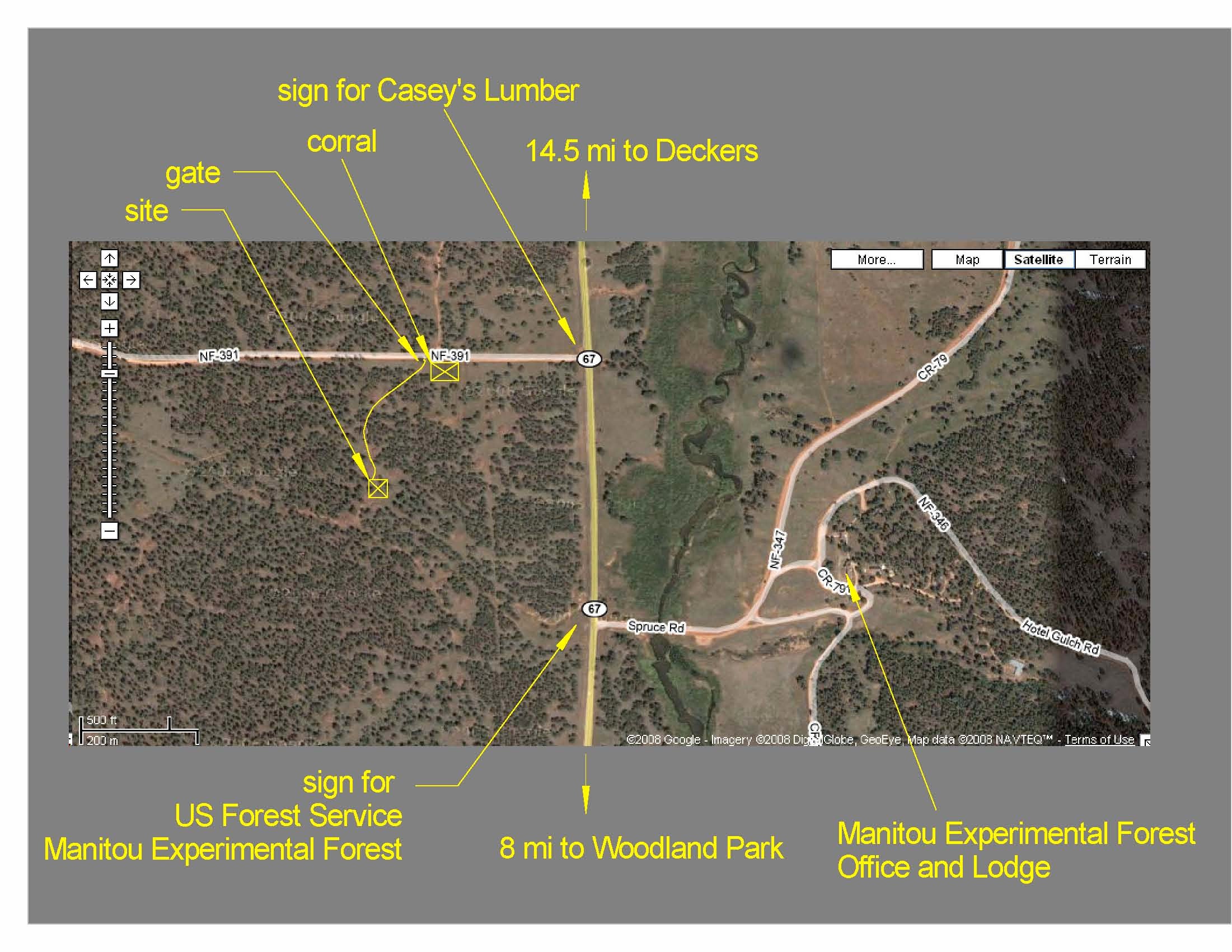
Click on the image for for a detailed satellite image of the site. |
BEACHON's Manitou Forest Observatory (MFO) is located in the US Forest Service’s Manitou Experimental Forest. The coordinates are 39.10065 N, 105.10250 W (+39° 6' 2.34", -105° 6' 8.94"; 2370 m, 7780 ft). The official address of the measurement site is: 589 F.S. Road 391 Woodland Park, CO.
MFO is located in a montane ponderosa pine zone in the Central Rockies, which is part of a larger zone that extends from Northern New Mexico to Southern Wyoming and is a component of the dominant Western U.S. ponderosa pine forest type that extends from Mexico to Canada. The site is representative of the semi-arid Western U.S. where biosphere-atmosphere exchange processes of energy, water, carbon, and nitrogen are particularly sensitive to changes in precipitation. While the site is located close to a major urban corridor (the Front Range Urban Corridor, which stretches from Pueblo, Colorado, north along Interstate Highway 25 to Cheyenne, Wyoming), measurements of trace gases and ambient aerosol at the site suggest that it is largely shielded from anthropogenic air masses due to its unique location in a north-south aligned valley separated from the Front Range Urban Corridor by the Rampart Range to the east, and Pike's Peak to the south; exceptions include episodic intrusions of anthropogenic air in evening downsloping air from the north. The site is located in a relatively flat valley with a reasonable upwind fetch, a topography that is amenable to performing flux measurements using micrometeorological techniques. The canopy is open and of varying density, with mixed-age ponderosa pine up to 100 years old and a surface cover of grasses, sage, crocus, forbs and exposed cryptogrammic soils.

Site Overview:
- The site is representative of the Central Rockies montane ponderosa pine zone that extends from Northern New Mexico to Southern Wyoming and is a component of the dominant Western U.S. ponderosa pine forest type that extends from Mexico to Canada.
- The site does not appear to be heavily impacted by Front Range urban air masses, based on a scoping study of key trace gases and aerosols performed by NCAR during March – November 2007.
- The site’s topography is amenable to performing flux measurements using micrometeorological techniques (i.e., it is relatively flat, with a reasonable upwind fetch).
- The site includes all essential infrastructure for hosting intensive measurement campaigns, including electricity, broadband internet, and limited on-site lodging as well as numerous food and lodging options located close-by in Woodland Park, CO.
- The site is easily accessed by researchers who reside in the Front Range urban corridor (e.g., two hours driving time from Boulder, CO).
Directions
Directions to the site from Colorado Springs: PDF
Directions to the site from Boulder: PDF
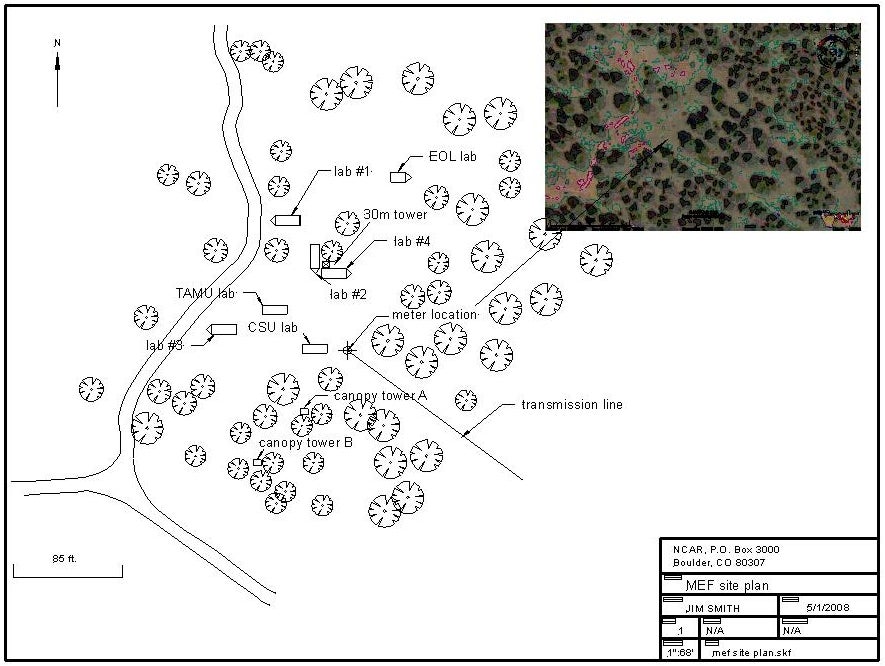
Site Plan
Below is a draft of the Site Plan (click on picture to view larger image):
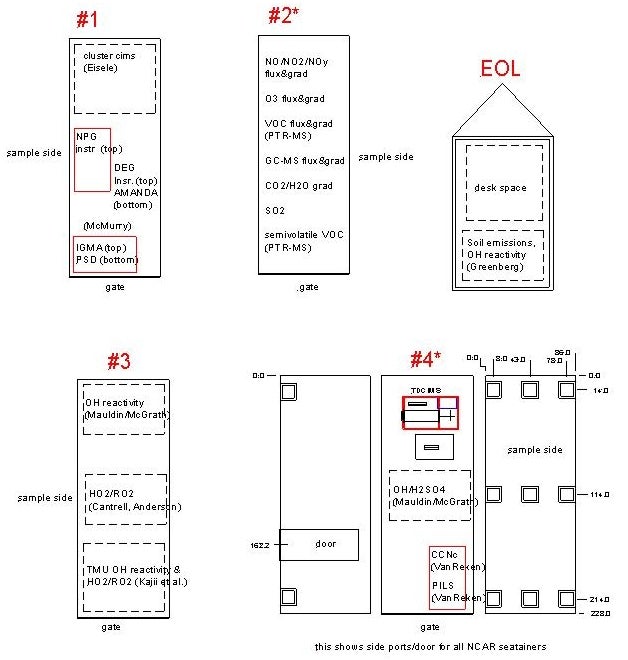
Laboratory space
The main laboratory space for BEACHON-SRM08 will be four 8’x20’ seatainers and one 8’x12’ trailer. Two other mobile laboratories will be provided by investigators from CSU and Texas A&M Univ. A draft laboratory plan is shown below:
Tower/canopy access
A 30 m walk-up tower will be designed and constructed for sampling the forest canopy, extending 15 m above the canopy. Access to tree branches in the upper and lower canopy will be provided by two shorter towers.
Electrical service
Three-phase, 208/120VAC electrical service will be provided at the site, with a total current capacity of 400 amps.
Network infrastructure
A line-of-sight connection to a wireless internet transceiver tower will be installed by a local internet provider, likely by mounting an antenna at the top of the tower. A local area network, web server, and file server will also be set up by NCAR personnel. Below are system details, which are patterned after the system being used at the NCAR Marshall Field Site.
- A central linux-based “gateway computer” with a fixed IP address will be the portal through which an internal network of all data acquisition systems operating at MEF (this will include systems operating on both linux and windows) will communicate with the outside world. This will connect to the web via the Motorola wireless system provided by McAfee Communications (the local ISP).
- This gateway computer will be an intermediate repository for all MEF data. This will be accomplished by configuring the gateway computer as a SAMBA file server.
- The gateway computer will transfer data to the main RAL database periodically, except for those mentioned under item 4, and use RAL database formatting protocols for storing the data.
- Some of our core measurements can be displayed as "real time web plots.” Examples include meteorology, trace gases such as O3, NOx and SO2, and aerosol size distribution.
- A selected number of the computers on the internal network may create "measurement status" screen dumps that we would like to have available for web viewing (maybe updated every 10 min. or something). This is being done for Marshall (I believe you need to log in to see this), and can also be done for MEF.
- The gateway computer will also provide a "standard clock" that all of the computers in the network can sync to.
- We will also provide the ability to connect to any computer on the internal network from outside (say, for example, a researcher from UC Berkeley who has deployed an experiment at MEF). That person can then run a remote desktop session on that computer, allowing them to change software parameters or do simple software-based diagnostics on their system. This remote desktop session will be served through the central gateway.
- The internal network will be a wired network, in which a hub is provided for each trailer or seatainer.
Additional Information
- Photographic tour: This photographic tour was created in 2007 by NCAR scientist Jim Smith.
- David Gochis' Field Notes: NCAR scientist David Gochis visited Manitou during April 2008 and summarized his observations in this document, with an emphasis on the hydrologic characteristics of the site.