Terra Trends: CO and AOD over industrial, fire-prone, and background regions
Two decades of carbon monoxide (CO) observations from the Measurements Of Pollution In The Troposphere (MOPITT) aboard the Terra satellite are used to evaluate atmospheric trends in carbon monoxide (CO). Hemispheric interannual variability in MOPITT CO is consistent with four other satellite instruments, lending confidence to our trend analysis. We build on the earlier trend analysis of Worden et al. (2013), expanding analysis to investigate 19 regions and including co-measured aerosol optical depth (AOD) from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument, to help interpret regional trends. The relative shorter chemical lifetime of aerosols means that AOD trends are more indicative of local drivers.
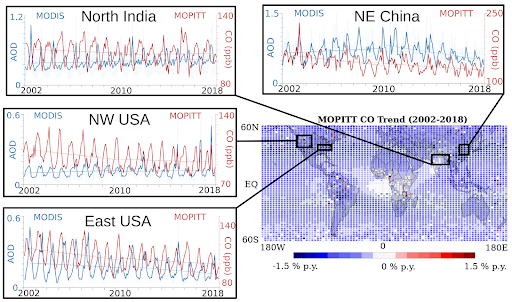
We find CO decreases globally at -0.50 % (±0.3 %) per year from 2002 to 2018. This is a deceleration compared to earlier studies over shorter periods. Local changes in biomass burning and anthropogenic contributions to air quality can counteract the global downward trend in CO. Regional analysis finds that trends in industrial regions reflect varying air quality controls. Additionally, fire emissions in Northern Hemisphere boreal regions (e.g. Northwest USA) counteract the decreasing CO in late summer. Analyses of trends by percentile and month indicate that the strongest (most negative) trends occur in the 75th percentile for the Northern Hemisphere and that late summertime CO trends (when CO lifetime is lowest) are the least substantial, in both hemispheres.
This work has been published in the Terra satellite 20-year special collection in the Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE) journal, and has contributed to the 6th Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Related CO trend work has also contributed to the Australian Government State of the Environment 2021 report, to be released in early 2022.
References:
Buchholz, R. R., Worden, H. M., Park, M., Francis, G., Deeter, M. N., Edwards, D. P., Emmons, L. K., Gaubert, B., Gille, J., Martínez-Alonso, S., Tang, W., Kumar, R., Drummond, J. R., Clerbaux, C., George, M., Coheur, P.-F., Hurtmans, D., Bowman, K. W., Luo, M., Payne, V. H., Worden, J. R., Chin, M., Levy, R. C., Warner, J., Wei, Z., and S., K. S., “Air pollution trends measured from Terra: CO and AOD over industrial, fire-prone, and background regions.” Remote Sensing of Environment, 256, 112275, doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.112275, 2021
Worden, H. M., Deeter, M. N., Frankenberg, C., George, M., Nichitiu, F., Worden, J., Aben, I., et al., (2013). “Decadal Record of Satellite Carbon Monoxide Observations.” Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 13: 837–50.