COVID-19 Impact on Air Pollution
With the development of the Covid-19 pandemic and the resulting slowdown in economic activity, anthropogenic emissions of primary pollutants were significantly altered for several months. We use the global Community Atmosphere Model with chemistry or CAM-chem to investigate the response of surface air quality in different parts of the world in response to modified emissions of primary pollutants during lockdowns (Gaubert et al., 2020). We applied emission adjustment factors to a global inventory to reflect the changes in the different sectors on a daily basis (Doumbia et al., 2020).
As an example, we show the time series of the CO emissions for a simulation with expected 2020 emissions (CONTROL) and a simulation that incorporates the adjustments factors (COVID) from January 1 2020 to June 1 2020. At the peak of the lockdowns over the United States of America, industry and transportation were reduced by 50 % and the residential emissions increased by 20 %. In this inventory, the transportation sector is estimated to contribute 65 % of the direct CO emissions; thus the transportation sector emerges as the main driver behind the decrease in CO emissions in the USA. A better understanding of the chemical processes that determine the oxidative potential of the atmosphere and their disruption during the pandemic should be therefore helpful in developing adequate measures to improve air quality.
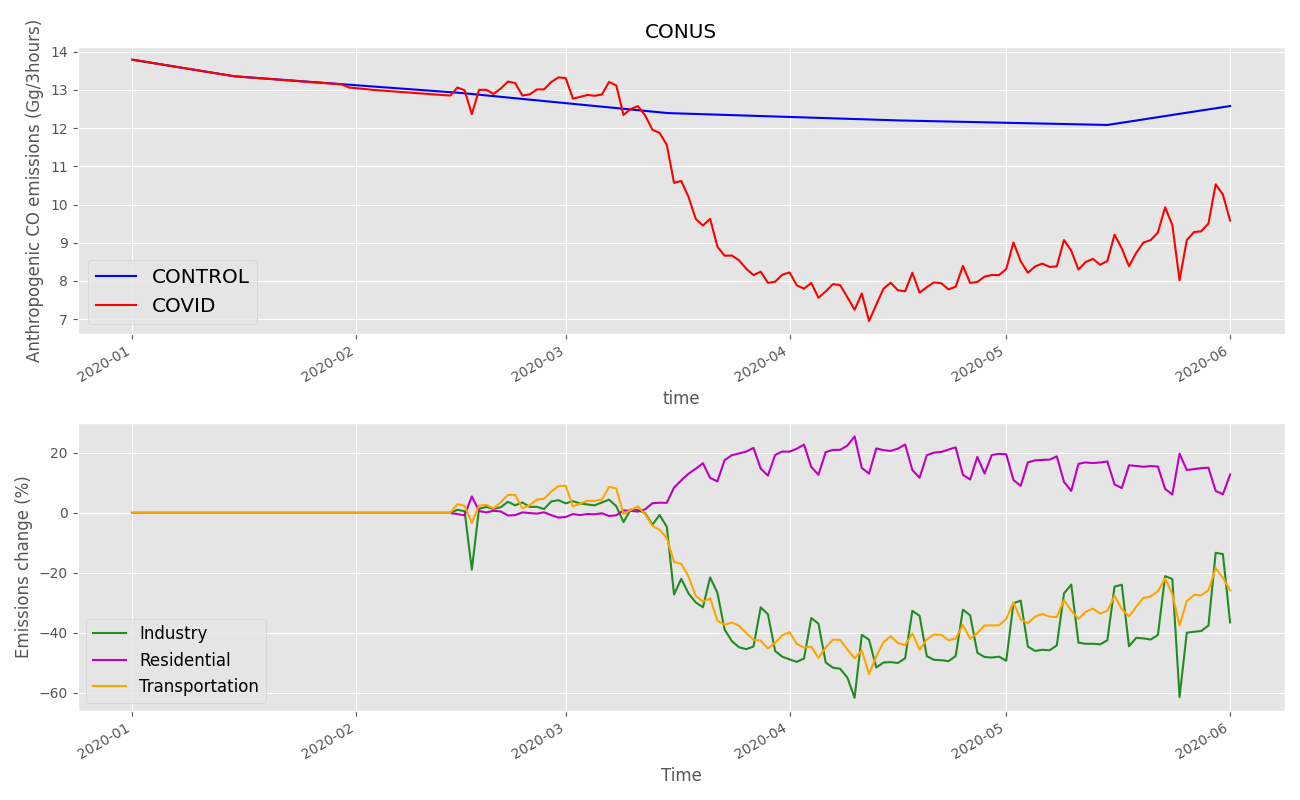
Figure 1: Top panel: 3 hourly emissions of anthropogenic CO from the CAMS (Version v4.2-R1.1), used as CONTROL, and the same emissions after daily sectoral adjustments were made to take the lockdown into account. Lower panel: Estimated relative changes in CO emissions due to the lockdowns in the USA by sectors.
References
Gaubert, B., Bouarar I., Doumbia T., Liu Y., Stavrakou T., Deroubaix A., Darras S., Elguindi N., Granier C., Lacey F., Shi X., Tilmes S., Wang, T. and G. P. Brasseur. Global Changes in Secondary Atmospheric Pollutants during the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic, submitted to Journal of Geophysical Research Atmosphere.
Doumbia, T., Granier, C., Elguindi, N., Bouarar I., Darras, S., Brasseur, G. P., Gaubert, B., Liu, Y., Shi, X., Stavrakou, T., Tilmes, S., and T. Wang. Changes in global air pollutant emissions during the Covid-19 pandemic: a dataset for atmospheric chemistry modeling, submitted to ESSD.