First Airborne Deployment and Results of the NCAR Trace Organic Gas Analyzer with a Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer (TOGA-TOF)
In the summer of 2019, the ACOM VOC Measurements Team, led by PI Dr. Eric Apel, deployed the NCAR Trace Organic Gas Analyzer with a Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer (TOGA-TOF) for the first time during the NASA/NOAA Fire Influence on Regional to Global Environments and Air Quality (FIREX-AQ) mission on board the NASA DC-8.
This successful first outing of the TOGA-TOF resulted in speciated observations of approximately 100 unique VOCs or VOC pairs over 23 research flights spanning from July 22 through September 5, 2019, sampling smoke from over 60 wildfires, prescribed burns, and agricultural fires in 17 different states in the western and southeastern regions of the United States. This was the largest number of species ever reported using the TOGA technique which previously employed a quadrupole mass spectrometer. The high resolution TOF mass spectrometer proved to have high utility in providing clear separation to allow for quantitation of individual VOC species in the extremely complex chemical soup of fire emissions. The TOF advantage will undoubtedly prove useful in ACOM and community led studies in the future. Figure 1 shows some correlations of TOGA-TOF measured species with CO in two different fire plumes during FIREX. The high quality TOGA-TOF data is providing important data that can be used to improve fire emissions models.
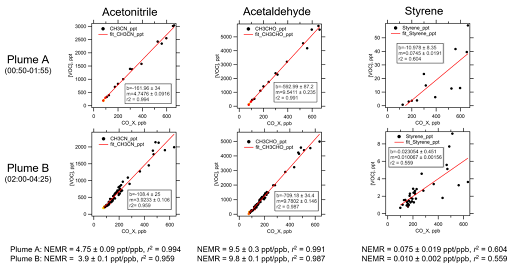
Figure 1. VOC to CO correlation plots for determining the normalized excess mixing ratios (NEMRs) to CO for three TOGA-TOF observed VOCs during two sequential lawn-mower sampling patterns (labeled Plume A and Plume B) of the Sheridan Fire in Arizona on August 17, 2019 (UTC). Slight differences in the fire chemistry between the first and second sampling patterns resulted in slightly different ratios of the observed VOCs to CO.